树的直径学习笔记
tsh_qwq
·
·
算法·理论
前言
死亡回放:
定义本身是简单的,引理本身是易懂的,但偏偏这玩意太会有机组合了。
——@VelvetChords
这个算法往往与其他算法组合在一起出题,包括 DP、并查集、LCA、二分等等。
定义
树的直径是指树上任意两点之间最长的简单路径。一棵树可以拥有多条直径,其长度相等。
以下图为例:
当然,这个图只是一个无权图,但是带权图的处理方法没啥区别,就不举例了。
是不是很简单?**但是**算法简单 $\ne$ 题目简单(这一点后面会印证的)。
## 求解
那么,我们要如何求解树的直径呢?
常用的方法有 **DFS** 和 **树状 DP**,好像也见过拿 **BFS** 求的,不过没去做具体了解,我们先讲这两种。
### DFS 法
DFS 法的优点在于好写(真的),缺点是无法用于**带有负边权**的树。
#### 步骤
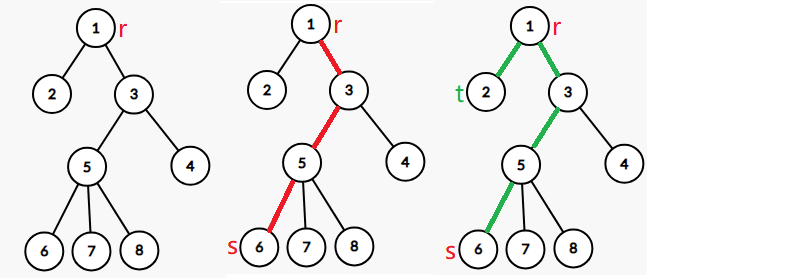
1. 从任意节点 $r$ 出发用 DFS 求出离它最远的节点 $s$。
2. 从 $s$ 出发求离 $s$ 最远的节点 $t$,则 $\delta(x,y)$ 为树的直径。
如下图所示:
#### 证明
**注:该部分内容参考了 OI Wiki。**
采用反证法进行证明,记第一次操作出发点 $r$,树真实的直径为 $\delta(s,t)$ ,假设离 $r$ 最远的节点 $x$ 不为 $s$ 或 $t$。
按照 $r$ 的位置进行分类讨论。
---
**情况 $1$:** $r$ 在 $\delta(s,t)$ 上:
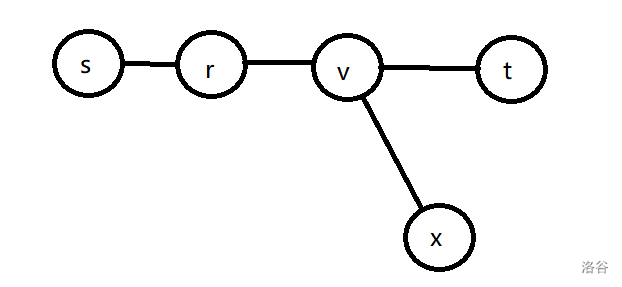
假设存在 $\delta(r,x) > \delta(r,t)$,则 $\delta(v,x) > \delta(v,t) \implies \delta(s,x)>\delta(s,t)$,与 $\delta(s,t)$ 为树上任意两点之间最长的简单路径矛盾。
---
**情况 $2$:** $r$ 不在 $\delta(s,t)$ 上,且 $\delta(r,x)$ 与 $\delta(s,t)$ 存在重合部分:
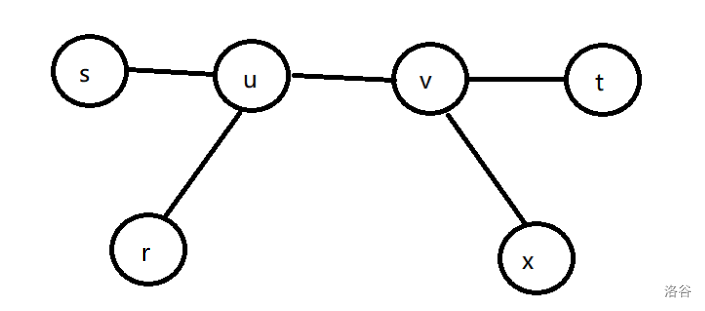
假设存在 $\delta(r,x) > \delta(r,t)$,则 $\delta(u,x) > \delta(u,t) \implies \delta(s,x)>\delta(s,t)$,与 $\delta(s,t)$ 为树上任意两点之间的最长简单路径矛盾。
---
**情况 $3$:** $r$ 不在 $\delta(s,t)$ 上,且 $\delta(r,x)$ 与 $\delta(s,t)$ 不存在重合部分:
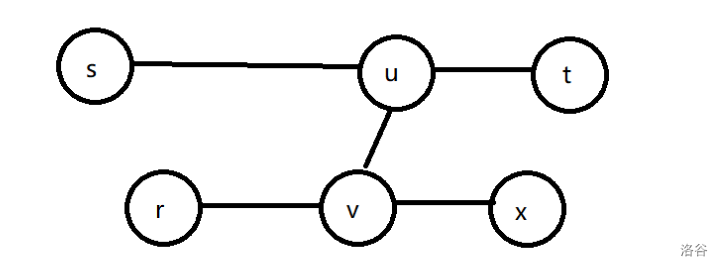
假设存在 $\delta(v,x) > \delta(u,t)$,则 $\delta(u,x) > \delta(u,t) \implies \delta(s,x)>\delta(s,t)$,与 $\delta(s,t)$ 为树上任意两点之间的最长简单路径矛盾。
---
综上,三种情况下均会产生矛盾,则在一棵树上,从任意节点 $r$ 出发进行一次 DFS,到达距离最远的节点一定是书的直径的一个端点。
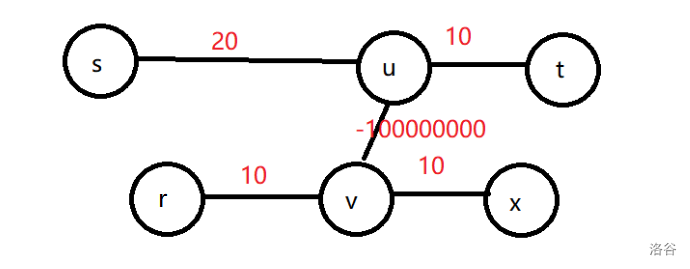
若边权带有负数,**情况 $3$** 无法证明,如下图。
#### 代码
此处给出 DFS 法的核心代码。
```cpp
void dfs(int u,int fa)
{
for(auto x:e[u])
{
int v=x.first,w=x.second;
if(v==fa)continue;
d[v]=d[u]+w;
if(d[v]>d[c])c=v;
dfs(v,u);
}
}
```
其中 $d_i$ 表示从 $r$ 出发到每个节点的距离。
---
### 树状 DP 法
树形 DP 法的优点是可以在**存在负权边的情况**下求解出树的直径。
#### 方法
我们记录当 $r$ 为树的根时,每个节点作为子树的根向下,所能延伸的最长路径长度 $f_1$ 与**和最长路径无公共边**的次长路径长度 $f_2$,那么直径长度就是 $f_1 + f_2$ 的最大值。
#### 代码
```cpp
void dfs(int u,int fa)
{
f1[u]=f2[u]=0;
for(int i=head[u];i;i=nxt[i])
{
int v=e[i];
if(v==fa)continue;
dfs(v,u);
int t=f1[v]+w[i];
if(t>f1[u])
{
f2[u]=f1[u];
f1[u]=t;
}
else if(t>f2[u])
{
f2[u]=t;
}
}
f[u]=f1[u]+f2[u];
if(f[u]>ans)ans=f[u];
}
```
## 性质
- 若树上所有边边权均为正,则树的所有直径中点重合(不一定恰好是某节点,可能是边上的任意一点)。
- **证明:** 使用反证法。设两条中点不重合的直径分别为 $\delta(s,t)$ 与 $\delta(s',t')$,中点分别为 $x$ 与 $x'$。显然,$\delta(s,x) = \delta(x,t) = \delta(s',x') = \delta(x',t')$。
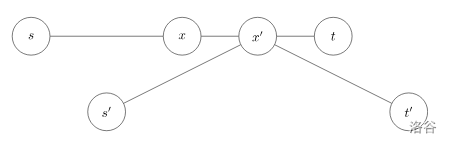
有 $\delta(s,t') = \delta(s,x) + \delta(x,x') + \delta(x',t') > \delta(s,x) + \delta(x,t) = \delta(s,t)$,与 $\delta(s,t)$ 为树上任意两节点之间最长的简单路径矛盾,故性质得证。
**注:引用自 [OI Wiki](https://oi-wiki.org/graph/tree-diameter/#%E6%80%A7%E8%B4%A8)。**
- 若两条直径有重叠部分,则于重叠部分同一段引出的两条直径的费重叠的部分长度相同。
- **图解:**
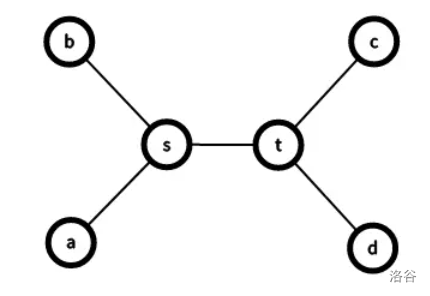
如上图,$\delta(b,s)=\delta(a,s),\delta(c,t)=\delta(t,d)$。
- **证明:** 设两条直线分别为 $\delta(a,c),\delta(b,d)$,重叠部分为 $\delta(s,t)$。($s$ 与 $t$ 可能重合,即 $s=t$)。
如果 $\delta(s,t) \ne \delta(s,b)$,此时若再得到 $\delta(s,t) \ne \delta(d,t)$,则取 $\delta(s,a)$ 和 $\delta(b,s)$ 中较长的一条(长度设为 $d_1$),$\delta(s,t)$ 和 $\delta(d,t)$ 中较长的一条(长度设为 $d_2$)。
若 $d_1$ 和 $d_2$ 不在同一条直线上,$d_1+\delta(s,t)+d_2>\delta(a,c)$,矛盾,若 $d_1$ 和 $d_2$ 在同一条直线上 $\delta(a,c) > \delta(b,d)$,出现矛盾。
## 模板
具体代码见上,[模板题链接](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/B4016)。
## 例题 1
例题一链接 [P4408](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P4408)。
hmm,这道题题面怎么这么长,看了半天才看懂。
题面省流:在一棵树上,找 $A,B,C$ 三个点,使得 $AB+BC$ 最大,并且 $AC>AB$(这点很重要)。
贪心一下可以得出我们只需先令 $AB$ 最大,再从 $B$ 出发寻找一个最长的 $BC$,但是一定要注意 $C$ 不能是 $A$!!!
所以我们只需先找出树的直径 $AB$,再从 $B$ 出发跑一次 DFS,最终答案就是 $\min(d_i,f_i)+k$。其中 $d_i$ 是 $A$ 至 $i$ 号点的简单路径长,$f_i$ 是 $B$ 至 $i$ 号点的简单路径长,$k$ 是 $AB$ 长,注意 $i$ 不能是 $A$ 或 $B$。
代码:
```cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
int n,m,c,d[200005],f[200005];
int first,last;
vector<pair<int,int>>e[200005];
void dfs(int u,int fa)
{
for(auto x:e[u])
{
int v=x.first,w=x.second;
if(v==fa)continue;
d[v]=d[u]+w;
if(d[v]>d[c])c=v;
dfs(v,u);
}
}
void dfs2(int u,int fa)
{
for(auto x:e[u])
{
int v=x.first,w=x.second;
if(v==fa)continue;
f[v]=f[u]+w;
if(f[v]>f[c])c=v;
dfs2(v,u);
}
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int u,v,w;
cin>>u>>v>>w;
e[u].push_back({v,w});
e[v].push_back({u,w});
}
dfs(1,0);
d[c]=0;
first=c;
dfs(first,0);
int k=d[c];
last=c;
dfs2(last,0);
int ma=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(i!=first&&i!=last)
ma=max(ma,min(d[i],f[i])+k);
cout<<ma;
return 0;
}
```
## 例题 2
[P3629](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3629)。
### 思路
这道题挺绕的,~~出题人吃枣药丸~~,说白了就是**在一颗树里找选 K 条路径,让它们不相交部分的长度最大**。
本题突破点在于 $1\le K \le 2$,所以我们只需要分类讨论一下。
#### K=1
拿原题里的图举例
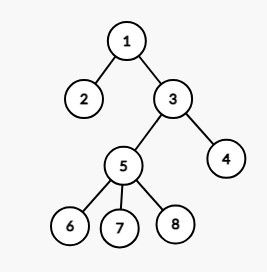
我们从节点 $1$ 出发,遍历整棵树,一开始每条边需要遍历 $2$ 次,即巡逻距离为 $2\times (n-1)$。
为了使巡逻距离变短,我们可以通过连接两个节点形成一条新的边,那么连什么边才能减少最多距离呢?
修建一条道路后,这棵树里就出现了一个环,我们定义 $S(x,y)$ 的为从 $x$ 到 $y$ 的距离,比如上面的图中 $S(1,6)=3$,我们从 $x$ 走到 $y$ 后,要再回到 $x$,这时如果我们在 $x$ 和 $y$ 之间连一条边,就可以减少 $(S(x,y)-1)$ 的距离,$-1$ 是因为要走新加的一条边,不难发现 $S(x,y)$ 的最大值就是**树的直径**的长度。
所以当 $K=1$ 时我们只需要找出树的直径并将其**首尾相连**即可得到答案,答案是 $(2\times n-L-1)$。
#### K=2
推完 $K=1$ 的情况,我们继续推 $K=2$ 的情况,经过第一次处理,我们的图变成了这样。
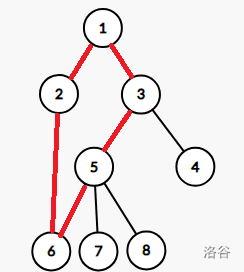
其中红色边是加入新的边之后形成的环。
但是我们需要再添加一条边,但是如果这两个点之间的路径与原先形成的环有重复的话,重复的部分就会计算两次,所以我们要令**不重叠的部分**长度最大。
题目原理就是这样,但是怎么去求第二条边缩减小的代价呢?我们可以将这个环上的边权改为 $-1$,再跑一次求直径,但是因为存在负边权,所以要用**树状 DP** 求。
### 代码:
```cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
int n,k,c,d[100005],fat[100005],fath[100005];
int f[100005],f1[100005],f2[100005];
int head,tail;
int ans;
vector<pair<int,int>>e[100005];
void dfs(int u,int fa)
{
for(auto x:e[u])
{
int v=x.first,w=x.second;
if(v==fa)continue;
d[v]=d[u]+w;
if(d[v]>d[c])c=v;
dfs(v,u);
}
}
void dfs2(int u,int fa)
{
for(auto x:e[u])
{
int v=x.first,w=x.second;
if(v==fa)continue;
fat[v]=u;
d[v]=d[u]+w;
if(d[v]>d[c])c=v;
dfs2(v,u);
}
}
void dfs3(int u,int fa)
{
f1[u]=f2[u]=0;
for(auto i:e[u])
{
int v=i.first,w=i.second;
if(v==fa)continue;
dfs3(v,u);
int t=f1[v]+w;
if(t>f1[u])
{
f2[u]=f1[u];
f1[u]=t;
}
else if(t>f2[u])
{
f2[u]=t;
}
}
f[u]=f1[u]+f2[u];
ans=max(ans,f[u]);
}
void dfs4(int u,int fa)
{
for(int i=0;i<e[u].size();i++)
{
int v=e[u][i].first;
if(v==fa||v!=fat[u])continue;
fath[v]=u;
c=v;
e[u][i].second=-1;
dfs4(v,u);
}
}
signed main()
{
// ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
// cin.tie(0);
// cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>k;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
e[u].push_back({v,1});
e[v].push_back({u,1});
}
dfs(1,0);
d[c]=0;
dfs2(c,0);
if(k==1)
{
cout<<2*n-d[c]-1;
return 0;
}
int an=d[c];
dfs4(c,0);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)fat[i]=fath[i];
//for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cout<<fat[i]<<" ";
dfs4(c,0);
// for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
// for(int j=0;j<e[i].size();j++)
// cout<<e[i][j].first<<" "<<e[i][j].second<<"\n";
// cout<<"\n";
// }
dfs3(1,0);
cout<<2*n-an-ans;
//cout<<endl<<an<<" "<<ans;
return 0;
}
```
## 常见错误
1. 函数套用错误。
```cpp
void dfs2(int u,int fa)
{
for(auto x:e[u])
{
int v=x.first,w=x.second;
if(v==fa)continue;
fat[v]=u;
d[v]=d[u]+w;
if(d[v]>d[c])c=v;
dfs1(v,u);//应为 dfs2(v,u)
}
}
```
2. $d_c$ 未归零。
```cpp
dfs(1,0);
//此处应有 d[c]=0;
dfs(c,0);
```
3. 遍历取最大值时未判断 $i$ 是否是直径两端。
```cpp
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
//此处应有 if(i!=first&&i!=last)
ma=max(ma,min(d[i],f[i])+k);
}
```
## 结语
终于写完了……
这个可恶的知识点主打一个算法简单,题目极难,还是要多练习的。
练习题嘛,直接在[洛谷搜一下好了](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/list?tag=213)(主要是我搜不到一个题单)。
update:补充证明过程。