使用线段树维护 $T_j$ 表示当前 $f_j - \operatorname{cost}_{j + 1, i} + \operatorname{val}_{j + 1, i}$ 的值。
依次枚举 $i \in [1, n]$,先更新 $\operatorname{cost}_{j + 1, i}$ 的值,即 $T_j \gets T_j - a_i (j \in [0, i - 1])$,再更新 $\operatorname{val}_{j + 1, i}$ 的值,即对于所有 $r_k = i$ 更新 $T_j \gets T_j + w_k (j \in [0, l_k - 1])$。于是 $f_i = \max(f_{i - 1}, \max\limits_{j = 0}^i T_j)$,$T_i \gets f_i$。
最终答案即为 $\max\limits_{i = 1}^n f_i$。
[AT_dp_w Intervals](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/AT_dp_w)
[[NOIP2023] 天天爱打卡](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P9871)
[[ZJOI2010] 基站选址](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P2605)
## 标记永久化
不用上传和下传标记。
如果区间修改完全覆盖了某节点,就更新其 tag,否则正常更新。那么在每个节点的 tag 中保存的就是对其子树整体所做的修改。因此查询时需要同时维护该点所有祖先节点的 tag 的合并结果。
但是使用场景有限制,比如不能处理受顺序影响的标记。
同时,因为可持久化线段树和树套树等数据结构无法下传标记,所以也需要标记永久化。
[「学习笔记」线段树标记永久化](https://www.cnblogs.com/yifan0305/p/17410471.html)
## zkw 线段树
不能优化时间复杂度的技巧都是奇技淫巧。需要结合标记永久化,除了卡常用处不大。
[算法学习笔记(76): zkw线段树](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/361935620)
[算法学习——zkw线段树](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/587648256)
[zkw线段树 模板整理与例题](https://blog.csdn.net/qcwlmqy/article/details/95938283)
# 图的连通性
主打一个感性理解。
参考:[【洛谷日报#237】Tarjan,你真的了解吗?](https://www.luogu.com/article/hnzykuxl),[图论基础 - Alex_Wei - 博客园](https://www.cnblogs.com/alex-wei/p/basic_graph_theory.html),<https://arxiv.org/pdf/2201.07197.pdf>,<https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~anupamg/advalgos17/scribes/lec02.pdf>。
## 强连通分量

[wiki](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tarjan's_strongly_connected_components_algorithm):
Each node v is assigned a unique integer v.index, which numbers the nodes consecutively in the order in which they are discovered. It also maintains a value v.lowlink that represents the smallest index of any node on the stack known to be reachable from v through v's DFS subtree, including v itself. Therefore v must be left on the stack if v.lowlink < v.index, whereas v must be removed as the root of a strongly connected component if v.lowlink == v.index. The value v.lowlink is computed during the depth-first search from v, as this finds the nodes that are reachable from v.
The lowlink is different from the lowpoint, which is the smallest index reachable from v through any part of the graph.
v.lowlink := min(v.lowlink, w.index) is the correct way to update v.lowlink if w is on stack. Because w is on the stack already, (v, w) is a back-edge in the DFS tree and therefore w is not in the subtree of v. Because v.lowlink takes into account nodes reachable only through the nodes in the subtree of v we must stop at w and use w.index instead of w.lowlink.
DeepL 翻译:
每个节点 v 都有一个唯一的整数 v.index,它按照节点被发现的顺序连续编号。它还会维护一个值 v.lowlink,该值代表栈中已知可通过 v 的 DFS 子树(包括 v 本身)从 v 到达的任何节点的最小索引。因此,如果 v.lowlink < v.index 则 v 必须留在堆栈上,而如果 v.lowlink == v.index 则 v 必须作为强连接组件的根节点被删除。v.lowlink 的值是在从 v 开始的深度优先搜索中计算出来的,因为这样可以找到从 v 可以到达的节点。
lowlink 与 lowpoint 不同,后者是 v 通过图的任何部分可到达的最小索引。
如果 w 在栈上,则 v.lowlink := min(v.lowlink, w.index) 是更新 v.lowlink 的正确方法。由于 w 已在堆栈上,(v, w) 是 DFS 树中的后沿,因此 w 不在 v 的子树中。由于 v.lowlink 考虑了只能通过 v 子树中的节点到达的节点,因此我们必须在 w 处停止更新,并使用 w.index 代替 w.lowlink。
------------
虽然我看不懂,但总之 zhw 讲的是错的。差评。
```cpp
int dfn[maxn], low[maxn], dfx = 0;
int scc[maxn], scccnt = 0;
std::stack<int> stack;
void tarjan(int u)
{
dfn[u] = low[u] = ++dfx;
stack.push(u);
for (int j = g.last[u]; j != 0; j = g.next[j])
{
int v = g.to[j];
if (dfn[v] == 0) tarjan(v), low[u] = std::min(low[u], low[v]);
else if (scc[v] == 0) low[u] = std::min(low[u], dfn[v]);
}
if (dfn[u] == low[u])
{
scccnt++;
while (1)
{
int t = stack.top();
stack.pop();
scc[t] = scccnt;
if (t == u) break;
}
}
return;
}
```
每个强连通分量中任意两个点都可以互相到达,缩点后形成有向无环图,可以进行 DP。计数、概率题记得判重边。
有时可能会发现题目最后需要求每个点在 DAG 中可达点个数,可以考虑在缩点前的图中发现性质,比如可到达的点都是一段连续区间,就可以在 DP 过程中转移左端点和右端点。
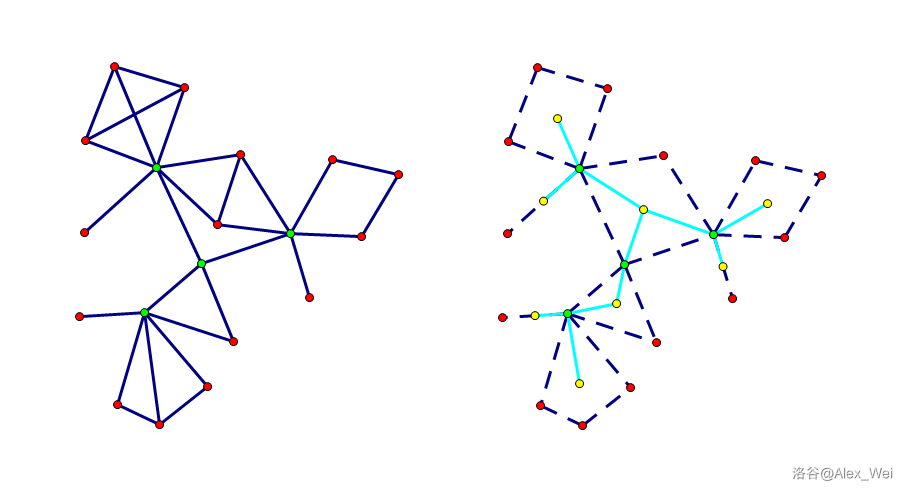
## 割点和桥

如图,无向图中只存在树边和返祖边,不存在前向边和横叉边。返祖边和被返祖边覆盖的树边都不是桥。
也因为非树边都是返祖边,所以求 Tarjan 割点和桥时不需要栈。
```cpp
int dfn[maxn], low[maxn], dfx = 0;
bool cut[maxn], bridge[maxm];
void dfs(int u, int fa)
{
dfn[u] = low[u] = ++dfx;
int son = 0;
for (int j = g.last[u]; j != 0; j = g.next[j])
{
int v = g.to[j];
if (v == fa) continue;
if (dfn[v] == 0)
{
son++;
dfs(v, u);
low[u] = std::min(low[u], low[v]);
if (low[v] >= dfn[u]) cut[u] = 1;
if (low[v] > dfn[u]) bridge[(j + 1) / 2] = 1;
}
else low[u] = std::min(low[u], dfn[v]);
}
if (fa == 0) cut[u] = son >= 2;
}
```
[[AHOI2005] 航线规划](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P2542)
使用树链剖分动态维护两点间桥的数量。因为只有不被非树边覆盖的树边是桥,所以可以维护区间内被覆盖次数的最小值和个数。
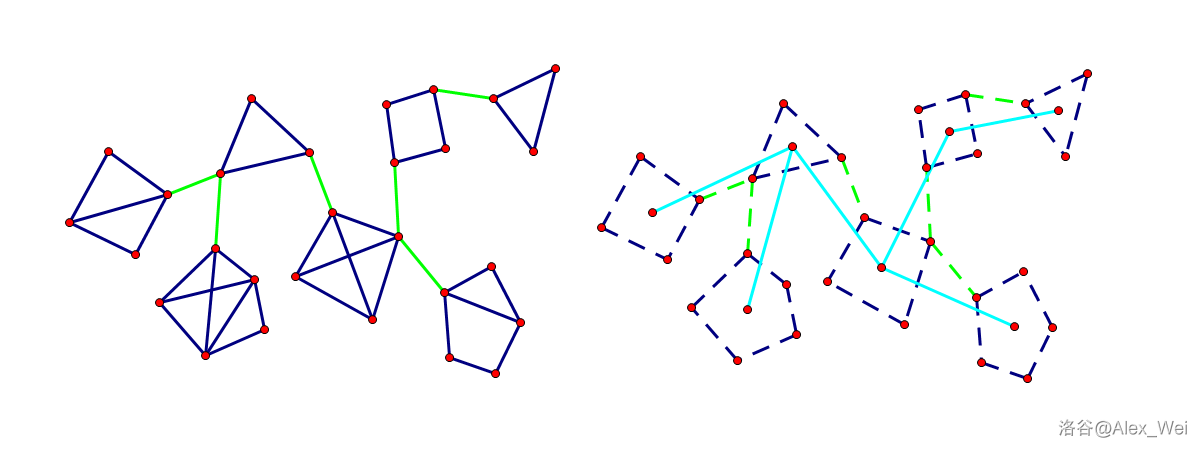
## 点双连通分量
每个割点会处于多个点双中,每条边则会处于唯一的点双。

找出点双有两种写法,~~洛谷题解区~~常见的一种是找出每个点所在的点双,但因为割点会处于多个点双,所以出栈时不能弹出其本身。
```cpp
int dfn[maxn], low[maxn], dfx = 0;
std::stack<int> stack;
std::vector<std::vector<int>> vdcc;
void tarjan(int u, int fa)
{
dfn[u] = low[u] = ++dfx;
if (g.last[u] == 0) { vdcc.push_back({u}); return; }
stack.push(u);
for (int j = g.last[u]; j != 0; j = g.next[j])
{
int v = g.to[j];
if (v == fa) continue;
if (dfn[v] == 0)
{
tarjan(v, u);
low[u] = std::min(low[u], low[v]);
if (low[v] >= dfn[u])
{
std::vector<int> t;
t.push_back(u);
int top;
do top = stack.top(), t.push_back(top), stack.pop();
while (top != v);
vdcc.push_back(t);
}
}
else low[u] = std::min(low[u], dfn[v]);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if (dfn[i] == 0) tarjan(i, 0);
```
又因为每条边都处于一个唯一的点双,也可以找出每条边所在的点双,再转换到点上。
```cpp
int dfn[maxn], low[maxn], dfx = 0;
std::stack<int> stack;
bool mark[maxm];
std::vector<std::set<int>> vdcc;
void tarjan(int u, int fa)
{
dfn[u] = low[u] = ++dfx;
if (g.last[u] == 0) { vdcc.push_back({u}); return; }
for (int j = g.last[u]; j != 0; j = g.next[j])
{
int v = g.to[j];
if (mark[(j + 1) / 2] == 0) stack.push((j + 1) / 2), mark[(j + 1) / 2] = 1;
if (v == fa) continue;
if (dfn[v] == 0)
{
tarjan(v, u);
low[u] = std::min(low[u], low[v]);
if (low[v] >= dfn[u])
{
std::set<int> t;
int top;
do top = stack.top(), stack.pop(), t.insert(g.st[top * 2 - 1]), t.insert(g.to[top * 2 - 1]);
while (top != (j + 1) / 2);
vdcc.push_back(t);
}
}
else low[u] = std::min(low[u], dfn[v]);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if (dfn[i] == 0) tarjan(i, 0);
```
虽然第二种写法比较冷门,但实际上更好用,因为点的信息不好转移到边上,但边的信息可以转移到点。
将每一个割点与其每一个所在的点双连边,缩边后形成 Block-Cut Tree(不是圆方树)。树上点双和割点交替出现。
[[POI2008] BLO-Blockade](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3469)
如果封锁某个非割点城镇,不会发生的访问活动为 $2 \times (n - 1)$ 个。如果封锁割点城市 $u$,依旧会发生的访问活动就只能在各个连通块中单独举行。因为割点会处于多个点双中,所以在统计某节点的子树大小时要减去它的子节点个数。
[[HNOI2012] 矿场搭建](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3225)
非割点坍塌没有影响,为避免割点坍塌只需要在点双缩点树上的每个叶子节点中任选一个设置救援出口。特别地,如果连通块本身就没有割点,需要两个救援出口。
## 边双连通分量
每个点都属于一个唯一的边双连通分量。记得判重边。
```cpp
int dfn[maxn], low[maxn], dfx = 0;
std::stack<int> stack;
std::vector<std::vector<int>> edcc;
void tarjan(int u, int fa)
{
dfn[u] = low[u] = ++dfx;
if (g.last[u] == 0) { edcc.push_back({u}); return; }
stack.push(u);
for (int j = g.last[u]; j != 0; j = g.next[j])
{
int v = g.to[j];
if ((j + 1) / 2 == fa) continue;
if (dfn[v] == 0)
{
tarjan(v, (j + 1) / 2);
low[u] = std::min(low[u], low[v]);
if (low[v] > dfn[u])
{
std::vector<int> t;
int top;
do top = stack.top(), stack.pop(), t.push_back(top);
while (top != v);
edcc.push_back(t);
}
}
else low[u] = std::min(low[u], dfn[v]);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if (dfn[i] == 0)
{
tarjan(i, 0);
if (!stack.empty())
{
std::vector<int> t;
while (!stack.empty()) t.push_back(stack.top()), stack.pop();
edcc.push_back(t);
}
}
```
缩点后每个边双是一个点,每个桥是一条边,形成一棵树。树上两点间的距离就是原图中两点间桥的个数。